Share this
On some mechanical equipment, it is often seen that the connection between the two machines is butted in the form of flanges. For example, part of the connection between the reducer and the motor is also connected through the flange. But there must be a gap in the connection, so how big is the gap between the flange connections, and what is the principle of sealing?
The gap between flange connections
Common detachable structures include flange connection, threaded connection and socket connection. Advantages and disadvantages of flange connection: flange connection has good strength and tightness, and it is suitable for a wide range of sizes and can be used in equipment and pipelines, so it is more common. However, when the flange is connected, it cannot be assembled and disassembled quickly, and the manufacturing cost is high.
Advantages and disadvantages of flange connection
Flange connection structure and sealing principle
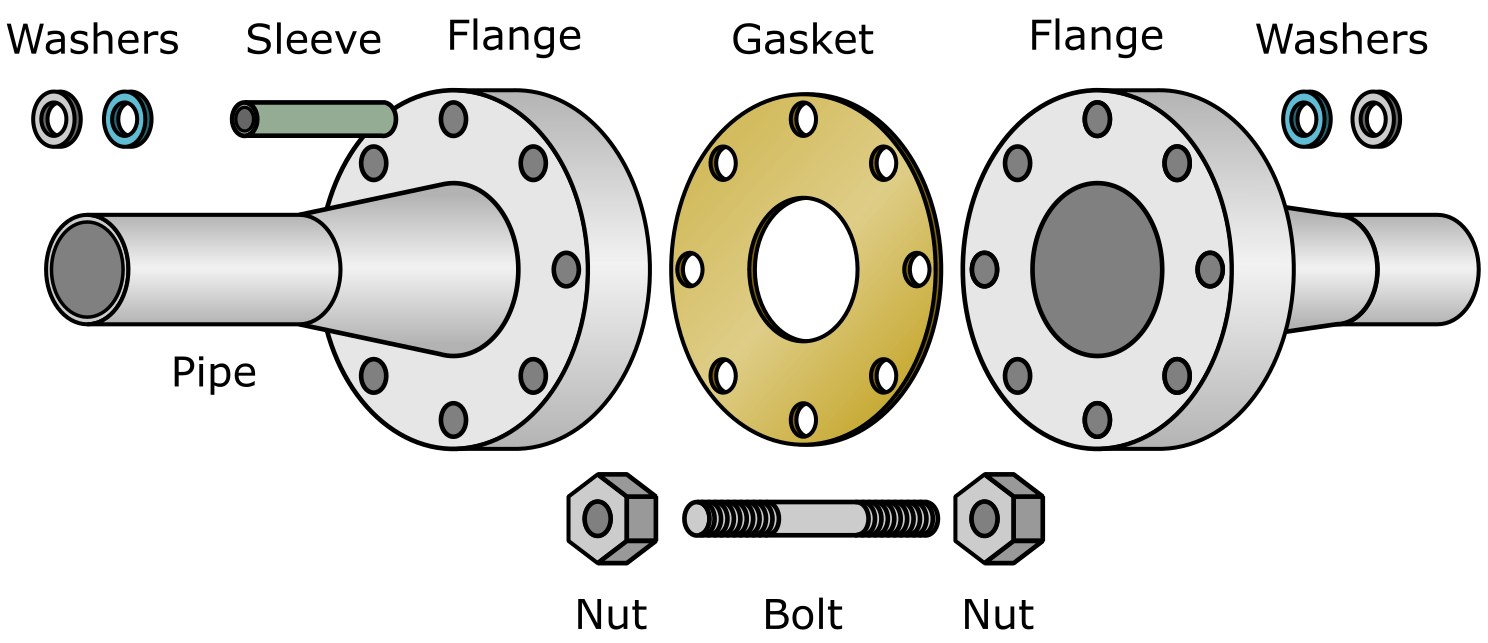
The flange connection structure is an assembly, which is composed of a pair of flanges, several bolts, nuts and a gasket. Therefore, the main problem to be solved in the design of the flange connection is to prevent medium leakage.
The principle of flange sealing: under the action of the bolt pre-tightening force, the flange compresses the gasket between the sealing surfaces. When the compression force per unit area of the gasket reaches a certain value, the gasket will deform. It is compacted to fill the unevenness on the sealing surface, thus forming an initial sealing condition for preventing the leakage of the medium. The required pressing force is called the preload sealing specific pressure of the gasket, and the unit is MPa.
The specific pressure of the preload seal is mainly determined by the gasket material.
In the working state, the axial force is stretched and the pressing force is reduced.
The gasket has sufficient resilience to compensate for deformation, and the specific pressure of the pre-tightening seal is not less than a certain value (the specific pressure of the working seal – the low specific pressure that must be retained between the sealing surface and the gasket so that the medium does not leak. ) to maintain a good seal.
On the contrary, if the rebound is insufficient, the specific pressure of the pre-tightening seal drops below the specific pressure of the working seal, or even if a gap reappears at the seal, the seal will fail.
Ensure that the screw flange connection is tight and leak-proof
It can be seen that in order to ensure the flange sealing, the specific pressure actually existing on the flange sealing surface must be not lower than the pre-tightening sealing specific pressure of the gasket during pre-tightening, and it should be higher than the working sealing specific pressure during operation.
Flat welding flange – the flange is welded on the equipment barrel or pipeline, which is easy to manufacture and widely used, but has poor rigidity.
After the flange is stressed, the rectangular section of the flange rotates slightly. The cylinder wall or pipe wall connected to the flange is deformed by bending. As a result, additional bending stress will be generated on the section of the cylinder wall near the flange. Therefore, the applicable pressure range of the flat welding flange is lower (PN<4.0MPa).
The principle of flange sealing
Butt welding flange – butt welding flange is also called high neck flange or long neck flange. The presence of the neck increases the rigidity of the flange and at the same time reduces the bending stress at the root because the root of the neck is thicker than the barrel. In addition, the connection between the flange and the cylinder, or the pipe wall is a butt weld. The strength of the fillet weld is better than that of the flat welding flange, so the butt welding flange is suitable for occasions with high pressure, high temperature or large equipment diameter.
Loose flanges—structures in which the flange is not directly fixed on the shell or cannot ensure that the flange and the shell as a whole bear the bolt load are classified as loose flanges, such as loose flanges, threaded flanges, etc. Flange, lap flange.
Looper flanges – flanges can be made of different materials from equipment or pipes, used for copper, aluminum, ceramics, graphite and other non-metallic materials
on the equipment or pipeline of the material.
There is no additional bending stress after being stressed, and it is only suitable for low-pressure occasions. Threaded flanges are widely used in high-pressure pipelines, and the additional stress generated by the flange on the pipe wall is small. However, this kind of flange has low rigidity and thick thickness and is generally only suitable for containers with low pressure. Arbitrary flanges are integrated with the shell, and their rigidity is worse than that of integral flanges, such as incomplete welded flanges.
Circular flanges are more common, and square flanges are useful for arranging pipes compactly. Oval flanges are usually used for
Valves and small-diameter high-pressure pipes.
Type A flat welding flange – it is directly welded to the barrel or head of the container. A certain additional bending moment will act on the vessel wall during both tightening and working.
And the rigidity of the flange itself is also small. Therefore, it is suitable for the range of lower pressure levels and smaller cylinder diameters.
B-type flat welding flange – B-type flange has a cylindrical short joint with a wall thickness of not less than 16mm. With this short joint, the rigidity of the entire flange can be increased, and the wall of the container can be prevented from bearing Additional bending moment. Therefore, it is suitable for larger diameters and higher pressure conditions. The larger diameter range for the PN0.25-1.6 pressure class can also be used for the smaller diameter range in the 2.5 and 4.0 pressure classes. The applicable full diameter range is 300-3000mm, and the temperature range is -20℃-350℃.
Long Neck Butt Welding Flange – It replaces the short joint in the B-type flat welding flange with the thickened neck at the root, thereby effectively increasing the overall rigidity of the flange, and the flange and the equipment are connected by butt welding, so it is used for higher pressure range (PN 0.6MPa-6.4MPa) and diameter range (DN300mmX2000mm), and the applicable temperature range is -20℃-450℃.
The specifications of the B-type flat welding flange below DN 2000mm have been included in the specified range of the long neck butt welding flange.
The connection size and flange thickness of these two flanges are exactly the same. Therefore, the B-type flat welding flange below DN2000mm can be replaced by the rolled long neck butt welding flange to reduce the production cost of the flange.
The above-mentioned classification of several kinds of flanges. Some of these flanges are commonly used and some are not commonly used. The form of the flange is selected according to the needs of the equipment so that the connection between the two pieces of equipment is more secure.
For pipe fittings, please link: https://bekingpiping.com

