Share this
Flange Inspection Process:
Flanges are important components used to connect pipelines, valves, equipment, and accessories, and their quality directly affects the safety and normal operation of the pipeline system. Therefore, it is crucial to inspect flanges. Here are the steps involved in the flange inspection process:
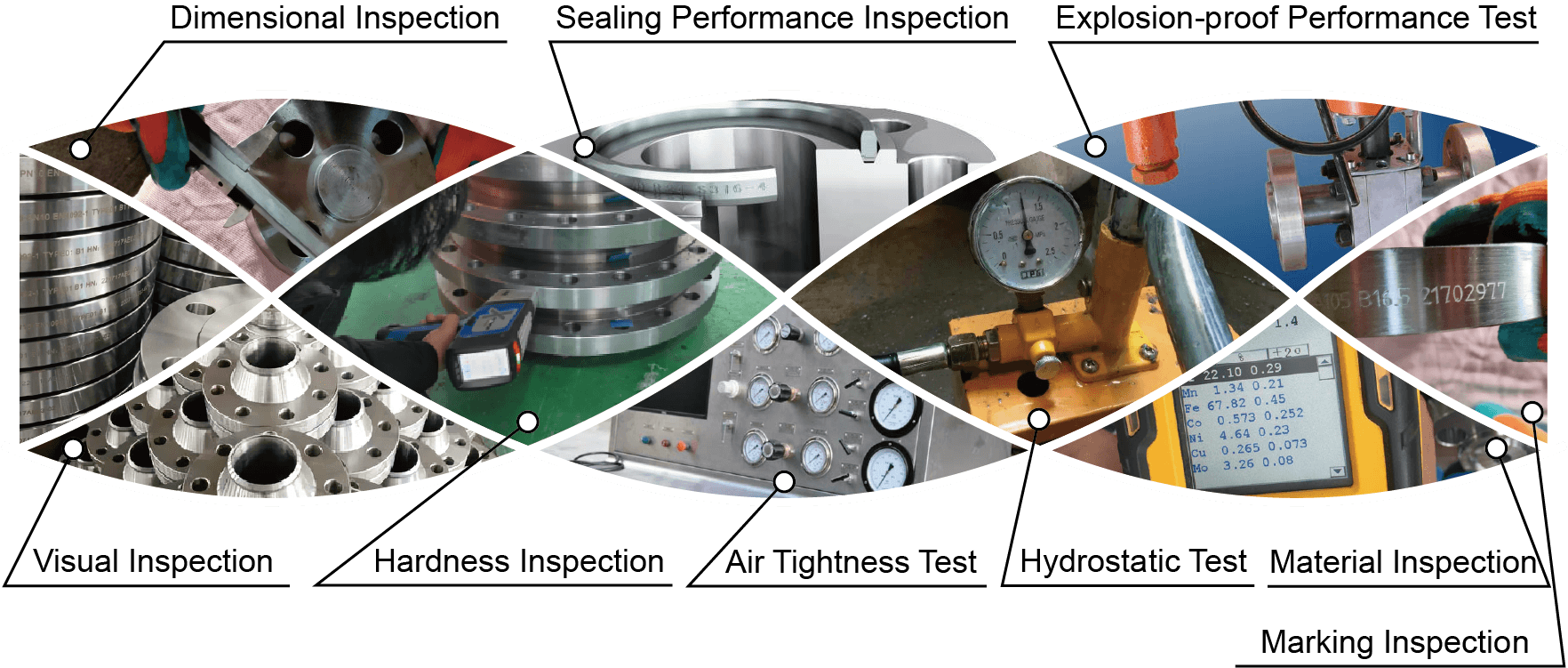
Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the flange surface, including checking for surface defects such as unevenness, cracks, sand holes, bubbles, scratches, and rust.
Dimensional Inspection: Measure various dimensions of the flange, such as inner diameter, outer diameter, bolt hole distance, bolt hole quantity, etc., and compare them with the standard dimensions to determine if the flange meets the standard requirements.
Hardness Inspection: Inspect the surface hardness of the flange to ensure that its hardness value is within the standard range.
Sealing Performance Inspection: Test the sealing performance of the flange, mainly including the following aspects:
(1) Hydrostatic Test: Use a hydrostatic test machine to perform a hydrostatic test on the flange. The test pressure and time should meet the standard requirements.
(2) Air Tightness Test: Use an air tightness tester to perform an air tightness test on the flange. The test pressure and time should meet the standard requirements.
(3) Explosion-proof Performance Test: Test the explosion-proof performance of the flange to ensure that it can withstand the explosion pressure that may occur in the pipeline system.
Material Inspection: Inspect the material of the flange to determine if it meets the standard requirements.
Marking Inspection: Inspect the marking of the flange to confirm that it is clear, accurate, and meets the standard requirements.
The above are the general steps in flange inspection, and the specific inspection methods and standard requirements should be determined based on different application scenarios and flange types.
For pipe fittings, please link: https://bekingpiping.com

