Share this
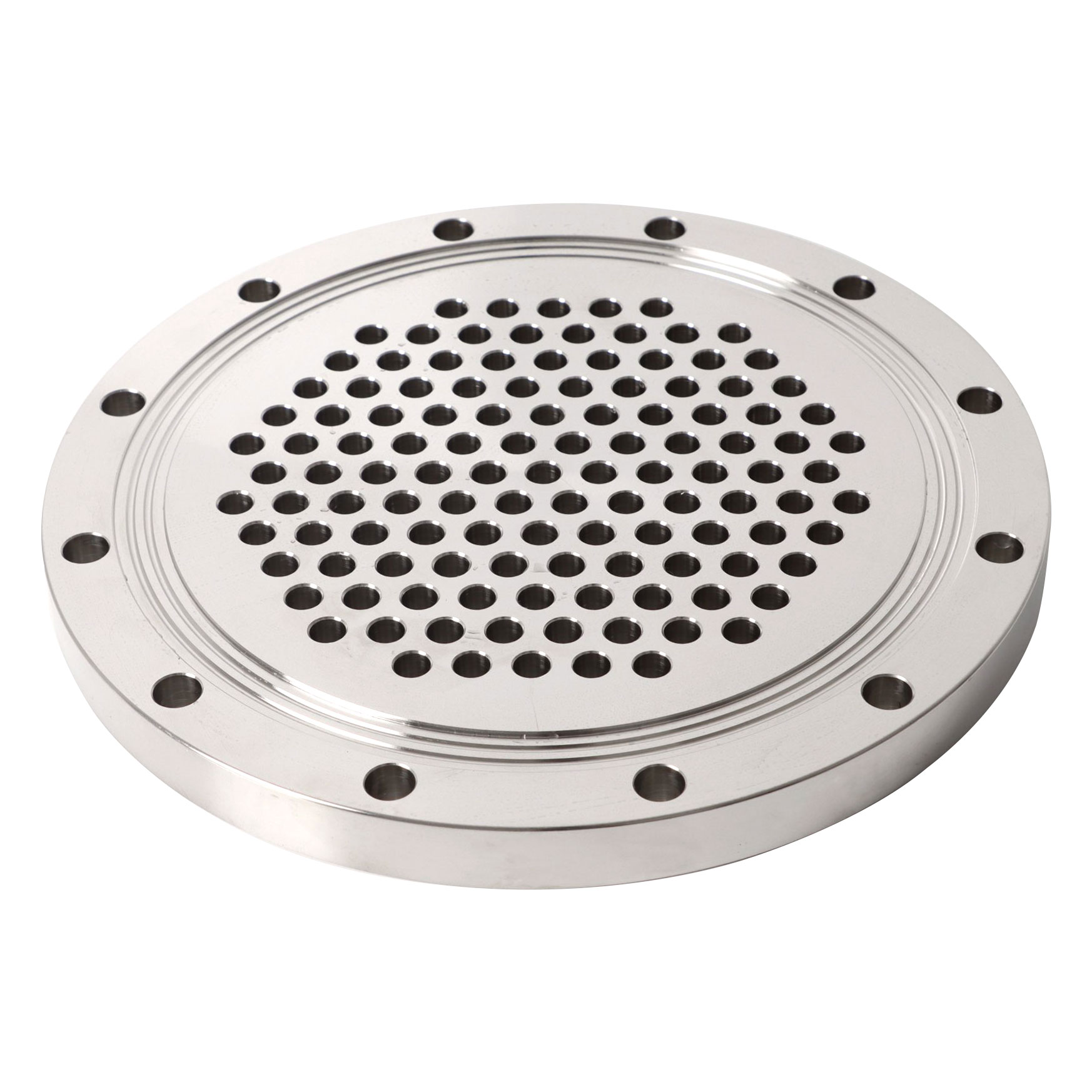
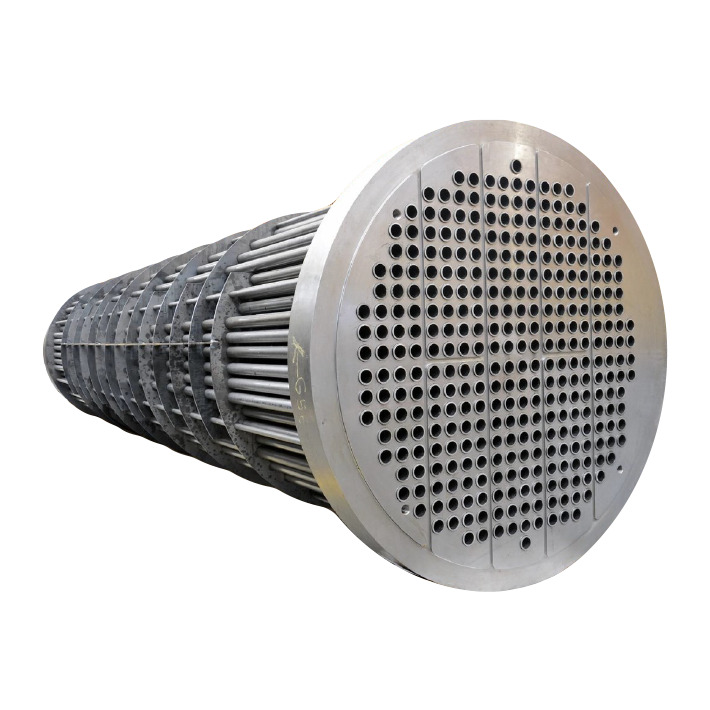
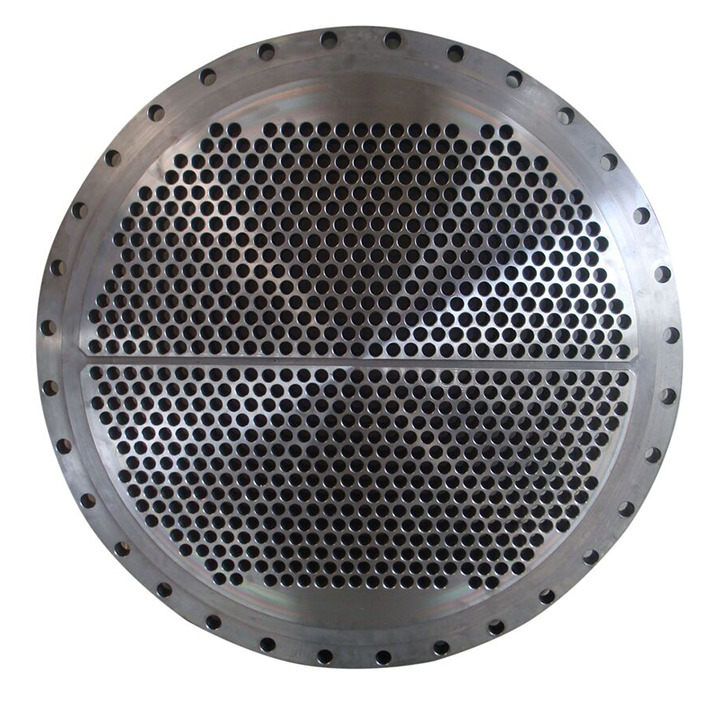
A tube sheet is usually made from a round flat piece of plate, a sheet with holes drilled to accept the tubes or pipes in an accurate location and pattern relative to one another. The tube sheets are used to support and isolate tubes in heat exchangers and boilers or to support filter elements. Tubes are attached to the tube sheet by hydraulic pressure or by roller expansion.
A tubesheet may be covered in a cladding material that serves as a corrosion barrier and insulator. Low carbon steel tube sheets can include a layer of a higher alloy metal bonded to the surface to provide more effective corrosion resistance without the expense of using the solid alloy, which means it can save a lot of costs. Perhaps the best-known use of tube sheets is as supporting elements in heat exchangers and boilers. These devices consist of a dense arrangement of thin-walled tubes situated inside an enclosed, tubular shell.
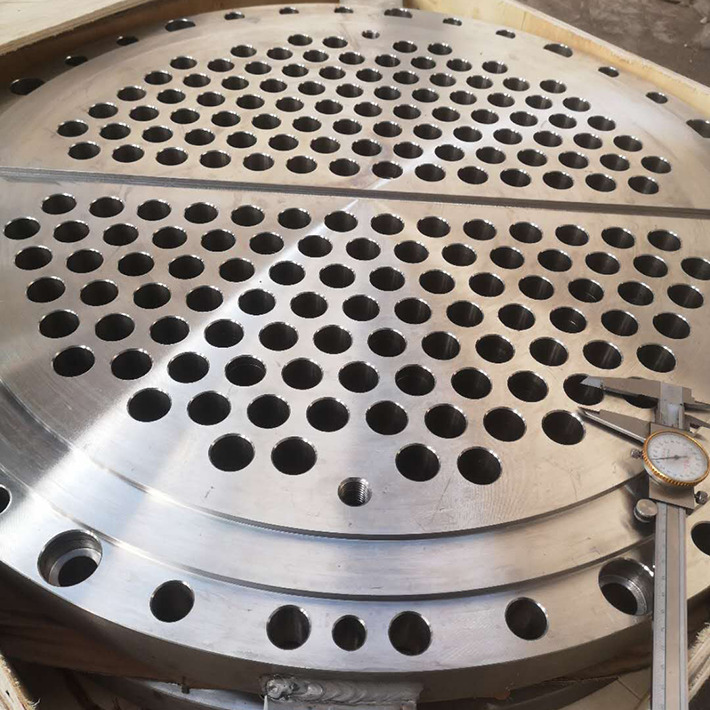
Tubes are supported on either end by sheets which are drilled in a predetermined pattern to allow the tube ends to pass through the sheet. The ends of the tubes which penetrate the tube sheet are expanded to lock them in place and form a seal. The tube hole pattern or “pitch” varies the distance from one tube to the other and the angle of the tubes relative to each other and to the direction of flow. This allows the manipulation of fluid velocities and pressure drop and provides the maximum amount of turbulence and tube surface contact for effective Heat Transfer.
In cases where it is critical to avoid fluid intermixing, a double tube sheet can be provided. The design of tube sheets is a fairly precise and complex process; the exact number of tubes needs to be established and a pattern of holes is calculated to spreads evenly over the tube sheet surface. Large exchangers may have several thousand tubes running through them arranged into precisely calculated groups or bundles. Sheet design and production are largely automated these days with computer software (like CAD) performing the calculations and the tube sheet drilling done on computer numerical control (CNC) machines. In this design, the outer tube sheet is outside the shell circuit, virtually eliminating the chance of fluid intermixing. The inner tube sheet is vented to the atmosphere so any fluid leak is easily detected. we can provide the best quality tube sheet for you.


Customized according to the drawings
Material:
Stainless Steel、Carbon Steel、Titaniumtim、Composite Plate、Nickel Base Alloy.
Tubesheet is one of the main components of shell-and-tube heat exchangers. It is used to arrange heat exchangers to separate the tube-side, and shell-side fluid, at the same time, it is affected by the tube-side and shell-side pressure and temperature. The following is the entire operation process of our factory.
1. Lathe processing tube sheet
2. marking and dot
3. drilling processing
4. Welded joints: including welds, fusion zones, heat-affected zones
Weld: It is formed by the solidification and crystallization of liquid metal in the molten pool. It usually consists of filler metal and a part of the base metal.
Fusion zone: The heating temperature is between the solid phase and the liquidus of the alloy, and the chemical composition and microstructure are not uniform, so it is thin and easy to produce weld cracks.
Heat-affected zone: the base metal on both sides of the weld, where the metallographic structure and mechanical properties change due to the welding heat. Two opposite weldings by manual argon arc welding or arc welding
5. Tube expansion The tube end portion of the tube extending into the tube plate is extruded by the expander, and the tube end is plastically deformed, and the tube plate hole simultaneously generates a certain pressing force, and is adhered together to achieve the purpose of sealing and fastening connection.
6. Cleaning Clean the surface of the tube head tube to prevent the dirt and other dirt from affecting the experimental results.
For pipe fittings, please link: https://bekingpiping.com